The F1 Engine – Heart of Formula One Racing
By Shenron on Apr 03, 2008 with Comments 0
Historically, engines built for Formula One racing were not designed to withstand more than a single race. But today, the Federation of International Automobiles also know as the FIA required that race car engines be uniquely designed to endure numerous races while still being able to produce maximum performance during competitions. Though modern technology can already provide means of attaining these requirements, engine failure still remains as a top reason why engines needed to be continuously replaced.
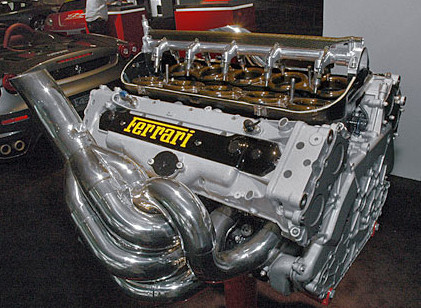
Engine specifications for Formula One racing have always been in a state of change since its early beginnings. For more than fifty years ago, a hundred BHP per liter was the expected result from an F1 engine. Ever since then, many changes have occurred. At present, the expected output is more or less 300 BHP per liter through the use of a 2.4 liter V8 engine. In addition, engines nowadays can utilize 650 liters of air per second. During a race, recent engines are expected to use up approximately 75 liters per 100 kilometers.
Formula One engines are built much smaller than a regular car engine. The usual car engines used by the average type of car consumers cannot display the same speed as F1 engines can. Drag reduction is an important aspect of Formula One that’s why in size, the latter’s engine is constructed smaller to also consequently allow it to take up minimal space.
Moreover, gearboxes are also an added feature found in F1 engines. The gears are placed behind the steering wheel so as not to distract the driver during a race. Nowadays, there are seven speed gearboxes commonly being used. Electronic controls are being used to activate transmissions on F1 engines.
When it comes to the type of energy, fuel is not much of a fuss for F1 engines. Normal gasoline, which is typically obtained from local gas stations, is actually used to refuel racecars on track. It is only during diagnostics when fuel becomes important and vital for an F1 engine. During diagnostics, mechanics check what kind of metals appear from leftover oil and fuel to determine the worn-out rate of the engine.
To be able to stop the illegal rigging done to F1 engines, the FIA placed penalties for creating expensive wear and tear engines in 2005. A penalty of ten places in a race is given if a team’s engine cannot be used after two Grands Prix.
Composed of almost 5,000 parts, a Formula One engine can truly be considered as one of the most expensive yet amazing machines. Its ability to make 20,000 revolutions a minute is the key to racecars extraordinary ability for speed and power. As these engines continuously evolve and change, they in themselves will serve as catalysts for a whole Formula One racetrack evolution.
Filed Under: General